
Nitrogen oxides nitric acid and ozone can all readily enter the lungs where they create serious damage to delicate lung tissue. Nitrogen oxides are critical components of photochemical smog.
UK annual emissions of nitrogen oxides by 2019 major emissions sources.
Nitrogen oxides sources and effects. Atmospheric constituents such as nitrogen oxides can be stratified vertically in the atmosphere. Ott noted that the lightning-produced NO x is typically found at altitudes greater than 5 km while combustion and biogenic soil NO x are typically found near the sources at near surface elevation where it can cause the most significant health effects. Overview Health effects Environmental effects Sources of emissions References Description Oxides of nitrogen are a mixture of gases that are composed of nitrogen and oxygen.
Two of the most toxicologically significant compounds are nitric oxide NO and nitrogen dioxide NO2. Other gases belonging to this group are nitrogen monoxide or nitrous oxide N2O and nitrogen. Nitrogen oxides are critical components of photochemical smog.
They produce the yellowish-brown colour of the smog. They produce the yellowish-brown colour of the smog. In poorly ventilated situations indoor domestic appliances such as gas stoves and gas.
Nitrogen compounds have a very long history ammonium chloride having been known to HerodotusThey were well known by the Middle Ages. Alchemists knew nitric acid as aqua fortis strong water as well as other nitrogen compounds such as ammonium salts and nitrate salts. The mixture of nitric and hydrochloric acids was known as aqua regia royal water celebrated for its ability to dissolve.
Natural Effects of NO x. One prominent effect of excessive nitrogen oxides is acid rain. Acid rain is the product of a chemical reaction between sulfur dioxide SO 2 NO x water and oxygen to form sulfuric acid and nitric acid.
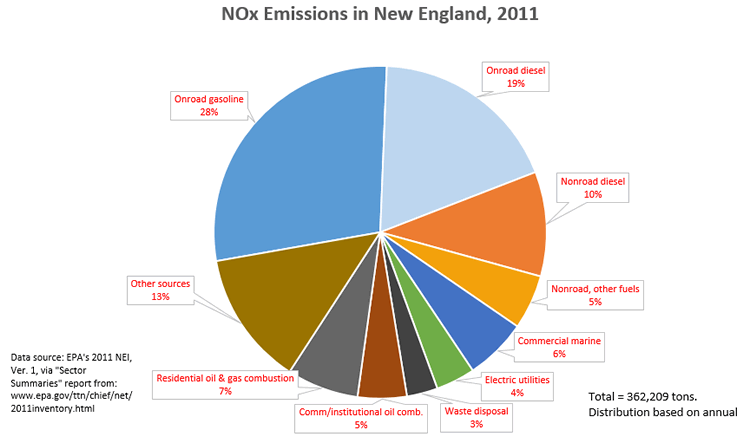
These reactants come together as industrial plants cars and generators release NO x and SO 2 into the air. Nitrogen oxides other than nitrogen dioxide have also been studied for possible adverse health effects. Chemical analysis of ambient aerosols collected in southern California has revealed that nitrates exhibit particularly high values as compared to other parts of the United States.
These aerosols are generally acidic in nature and are composed of nitric acid and nitrate salts that are formed. Major emission sources for nitrogen oxides in the UK Figure 7. UK annual emissions of nitrogen oxides by 2019 major emissions sources.
Although naturally produced nitrogen oxides outweigh man-made emissions NOx from natural sources are typically found at altitudes higher than 5km. Man-made emissions due to fossil fuel combustion either from stationary sources 24 and mobile sources 49 are typically found near the sources at near surface elevation where it can cause significant health effects. Fine particulate matter PM 25 particles with a mass median aerodynamic diameter of less than 25 micrometers in the atmosphere is associated with severe negative impacts on human health and the gases sulfur dioxide nitrogen oxides and ammonia are the main PM 25 precursors.
However their contribution to global health impacts has not yet been analyzed. Nitrogen dioxide and nitric oxide are referred to together as oxides of nitrogen NOx. NOx gases react to form smog and acid rain as well as being central to the formation of fine particles PM and ground level ozone both of which are associated with adverse health effects.
Sources of NOx Pollution. Smog is air pollution that reduces visibilityThe term smog was first used in the early 1900s to describe a mix of smoke and fogThe smoke usually came from burning coalSmog was common in industrial areas and remains a familiar sight in cities today. Today most of the smog we see is photochemical smogPhotochemical smog is produced when sunlight reacts with nitrogen oxides and at least.
Nitrogen oxides nitric acid and ozone can all readily enter the lungs where they create serious damage to delicate lung tissue. Even short-term exposure can irritate the lungs of healthy people. Ground-level ozone is formed by photochemical reactions between sunlight and pollutant precursors such as nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds especially in warm conditions and peaks in summer temperatures.
66 Nitrogen oxides including nitrogen dioxide are formed primarily by the reaction of ozone with nitric oxide emitted during fossil fuel combustion. As a result steep. What Is Nitrogen Dioxide.
Nitrogen dioxide or NO 2 is a gaseous air pollutant composed of nitrogen and oxygen and is one of a group of related gases called nitrogen oxides or NOxNO 2 forms when fossil fuels such as coal oil gas or diesel are burned at high temperatures. NO 2 and other nitrogen oxides in the outdoor air contribute to particle pollution and to the chemical reactions that. Nitrogen is the most abundant element in the air and is essential to plant and animal life.
Sources of nitrogen from human activities such as electric power generation industry transportation and agriculture can upset the natural balance of nitrogen in the environment. When fossil fuels are burned they release nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere which contribute to the formation of smog. Petrol and diesel-engined motor vehicles emit a wide variety of pollutants principally carbon monoxide CO oxides of nitrogen NO x volatile organic compounds VOCs and particulate matter PM 10 which have an increasing impact on urban air quality.
In addition pollutants from these sources may not only prove a problem in the immediate vicinity of these sources but can be transported. These six pollutants are carbon monoxide lead nitrogen oxides ground-level ozone particle pollution often referred to as particulate matter and sulfur oxides. Carbon Monoxide ATSDR Toxic Substances Portal.
Carbon Monoxide EPA Website external icon. Interaction Profile Carbon Monoxide Formaldehyde Methylene Chloride Nitrogen Dioxide Tetrachloroethylene. Nitrogen oxides are gases produced by fuel combustion.
They include nitric oxide NO which is rapidly converted to nitrogen dioxide NO2 after emission from vehicles and other sources. Exposures have been associated with lung irritation emergency department visits and hospital admissions for respiratory conditions. Nitrogen oxides also contribute to the formation of ozone.
Nitrogen dioxide is an important atmospheric trace gas not only because of its health effects but. On a global scale emissions of nitrogen oxides from natural sources far outweigh those generated by human activities. Natural sources include intrusion of stratospheric nitrogen oxides bacterial and volcanic action and lightning.
Because natural emissions are distributed over the entire. Tropospheric or ground-level ozone what we breathe is formed primarily from photochemical reactions between two major classes of air pollutants volatile organic compounds VOC and nitrogen oxides NOx. These reactions have traditionally been viewed as depending upon the presence of heat and sunlight resulting in higher ambient ozone concentrations in summer months.
Sources of Production. Photochemical reactions in the atmosphere that involve sunlight oxides of nitrogen and hydrocarbons. Effects on Humans and Environment.
There are seven oxides of nitrogen that may be found in the ambient air. Nitrous oxide N2O is a greenhouse gas with significant anthropogenic sources contributing to its worldwide abundance 03 ppm. However nitric oxide NO and nitrogen dioxide NO2 are the two principal nitrogen oxides associated with combustion sources.
Ambient concentrations of these two gases vary widely. Smog is a mixture of air pollutantsnitrogen oxides and volatile organic compoundsthat combine with sunlight to form ozone. Ozone can be beneficial or harmful depending on its location.
Sources of toxic explosive and asphyxiant gases. Gases in mines may be naturally occurring the products of combustion or fumes from vehicle exhaust emissions or activities such as blasting. They include methane and other hydrocarbons carbon dioxide carbon monoxide oxides of nitrogen sulphur dioxide hydrogen sulphide ammonia and radon.
Methane and other hydrocarbons encountered during. Nitrogen oxides or NO x is the generic term for a group of highly reactive gases all of which contain nitrogen and oxygen in varying amounts. Many of the nitrogen oxides are colorless and odorless.
Nitrogen oxides form when fuel is burned at high temperatures as in a combustion process. The primary sources of NO x are motor vehicles electric utilities and other industrial commercial.